Produced Water Treatment
Produced water has become a global environmental issue due to its huge volume and toxicity that may pose detrimental effects on receiving environment. The disposal of produced water during petroleum exploitation is known to cause serious environmental damage. In order to reduce the negative impact caused by produced water, it is necessary to perform a water treatment before disposing it into the environment.
Over tens of years, produced water treatment technologies have progressed from conventional processes to the most sophisticated methods of separation. Large tanks were used as the first attempt at gravity separation but were inefficient and required much space. As the industry matured, utilizing only a gravitation process with an adequate number of retention time tanks became difficult in the limited space available. Some technologies took strides toward improvement after that to enhance separation capability while decreasing the overall footprint of the equipment.

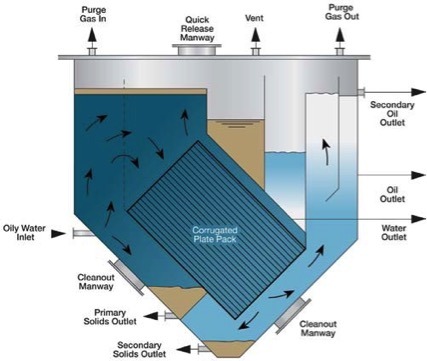
Corrugated Plate Interceptor (CPI)
Corrugated Plate Interceptor (CPI) provides economical and effective removal of oil and solids from produced water by gravity separation principle that is based on the difference of specific gravity between the phases (oil, solid, water).
The heart of Interceptor is its plate pack. The plate pack is designed to minimize the distance a free oil droplet must rise before coming into contact with other oil droplets. This design ensures that the oil droplets coalesce on the undersides of the corrugated plates, facilitating the free oil removal process.
The configuration and number of plates of the Interceptor units provide enough effective area for free oil removal with greater than 60 microns. While the separator between the plates is able to tolerate up to 100 ppm of total suspended solids without affecting the effluent quality.
Interceptor is often used as primary water treatment in order to process the produced water before the secondary treatment/flotation unit.
Application
- Better effluent quality – removes free oil droplets 60 microns or larger
- Superior solids handling – tolerates 100 ppm total suspended solids
- Compact Design
- Low maintenance design – no moving parts
- Continues Operation

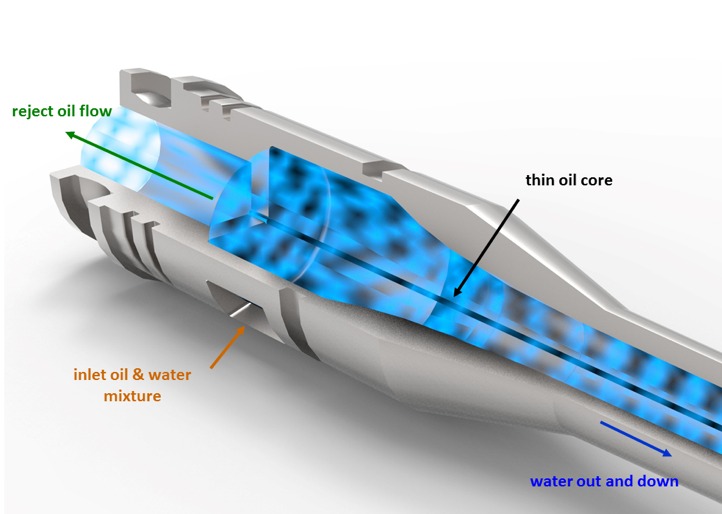
Deoiling hydrocyclone
In the basic design of the de-oiling hydrocyclone the phases to separate enter into the cyclone via a tangential inlet and by the effect of the wall curvature of the cylindrical body a strongly swirling stream is developed, causing the lighter phase to migrate toward the centreline and the heavier one toward the wall.
Hydrocyclone is an excellent coalescing device, and its functions best as primary treating device. It is a type of gravity unit that uses pressure to speed up and enhance the separation process, Hydrocyclone requires a minimum pressure of 100 psi to produce the required velocities. Hydrocyclone do not appear to work well with oil droplets less than 10 to 20 microns in diameter.
Application
- No moving part
- No Power (if High enough Pressure available)
- Small oily reject stream (1-3%)
- Compact Design
- Continues Operation
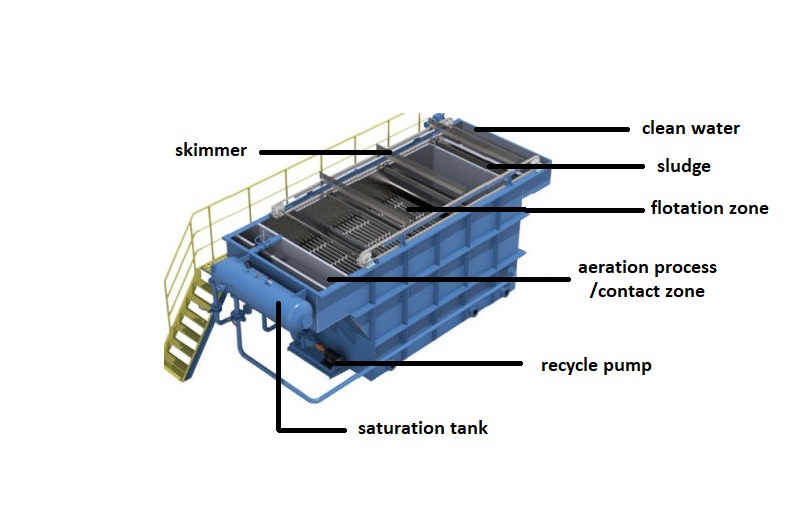
Dissolved air flotation (DAF) is often used after a primary gravity separator to enhance the quality of wastewater. The key to Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) is the dissolution of air (or other suitable gas) under pressure and the reduction of this pressure to form bubbles. DAF is suitable for the removal of light and small size of oil droplets that are difficult to settle. The generation of microbubbles contributes to removal efficiency. Additional chemicals is needed to enhance the efficiency.
Induced Gas Flotation (IGF) and Dissolved Gas Flotation (DGF)
Induced gas flotation (IGF) and Dissolved gas flotation (DGF) differ fundamentally in the way of generating gas bubbles. IGF/DGF is the most common method of removing oil from produced water before the disposal or reinjection into the reservoir. Their performance in each case was correlated with produced water characteristics and operational parameters.
In the IGF, gas bubbles utilized in the separation process have a diameter in the range of 100 – 1000 μm, while DGF have a diameter in the range of 10 – 100 μm.

Compact Flotation Unit (CFU)
Multistage single-vessel CFU is introduced by Triton Kencana Tirta where the number of internal stages can be adjusted to the PW quality at the inlet. CFU is a vertical vessel with a retention time of less than 1 minute. It is designed to maximize performance and minimized the footprint and weight.
The compact flotation unit uses gas flotation combined with centrifugal forces to separate and remove hydrocarbons as liquid and gas, aromatic compounds, hydrophobic substances, and small solid particles from produced water.
Application
- Minimal footprint and weight
- Optimal oil removal efficiency
- Simple operation.

Polishing/Filtration Unit
Produced water typically contains a lot of pollutants including hydrocarbons and metals, requiring proper management and treatment prior to its disposal. In addition, increasingly stringent environmental regulations, economic constraints, and the compatibility of water quality with injection well formation necessitate the use of more advanced treatment methods.
The concentration and particle size distribution of dispersed hydrocarbons and suspended solids are important characteristics and bear upon both water treatment and injectivity. Triton Kencana Tirta, deliver filtration unit for the reduction of dispersed hydrocarbons and suspended solids as a polishing unit, in a small footprint using both temporary and permanent installation. We provide both rental and new build equipment to efficiently solve your problems.
Equipment
- Activated Carbon Filter
- Multimedia Filter
- Oil Absorbent
- Nutshell Filter
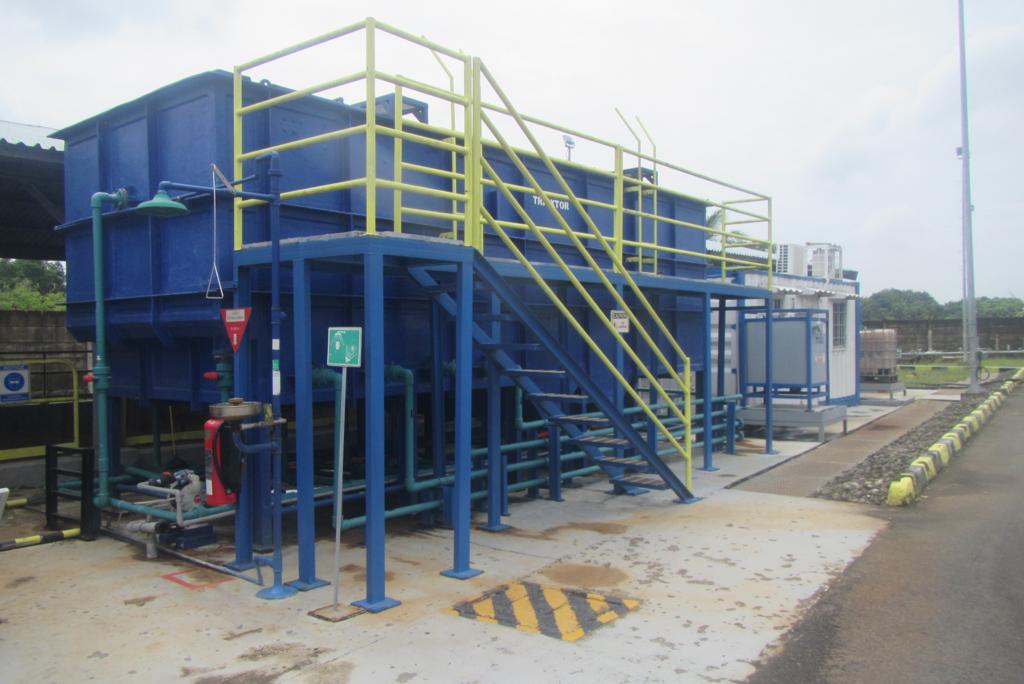

COD Removal
TRIOXTOR® is our registered technology design to efficiently remove COD contaminant coming from produced water. With proper pre-treatment, almost 95% of COD could be removed to achieve PERMENLH No. 19 Tahun 2010. Its compact and moveable design make it easy and efficient to be applied in the remote or limited space.

